5G vs wi-fi 6 – Which One is Better?
In the modern world, having wi-fi 6 connectivity is crucial. A fast and dependable internet connection is now essential, regardless of whether you’re managing a smart home, working remotely, playing video games online, attending Zoom meetings, or binge-watching your favorite shows. Stronger, quicker, and more effective wireless networks are required as our reliance on digital technology grows. 5G and Wi-Fi 6 are two of the most talked-about technologies in this field. These are significant advancements in data transmission and our interactions with the digital world, not merely improvements to current technologies. On the surface, 5G and Wi-Fi 6 both offer ultra-fast speeds, minimal latency, increased network efficiency, and compatibility for more devices.
However, they are essentially distinct technologies designed for different situations. The newest cellular network technology, 5G, was created to provide mobile internet access while on the road. In contrast, Wi-Fi 6 is the most recent iteration of wireless local area networking (WLAN), designed for high-performance connectivity in public areas, workplaces, and residences. We’ll outline the main distinctions between 5G and Wi-Fi 6 in this blog post, evaluate how well they work in practice, examine their advantages and disadvantages, and assist you in determining which—or both—deserves a place in your connected life.
What is a 5G network?
The fifth-generation mobile network, or 5G, is the replacement for 4G LTE. This cellular technology was created to provide:
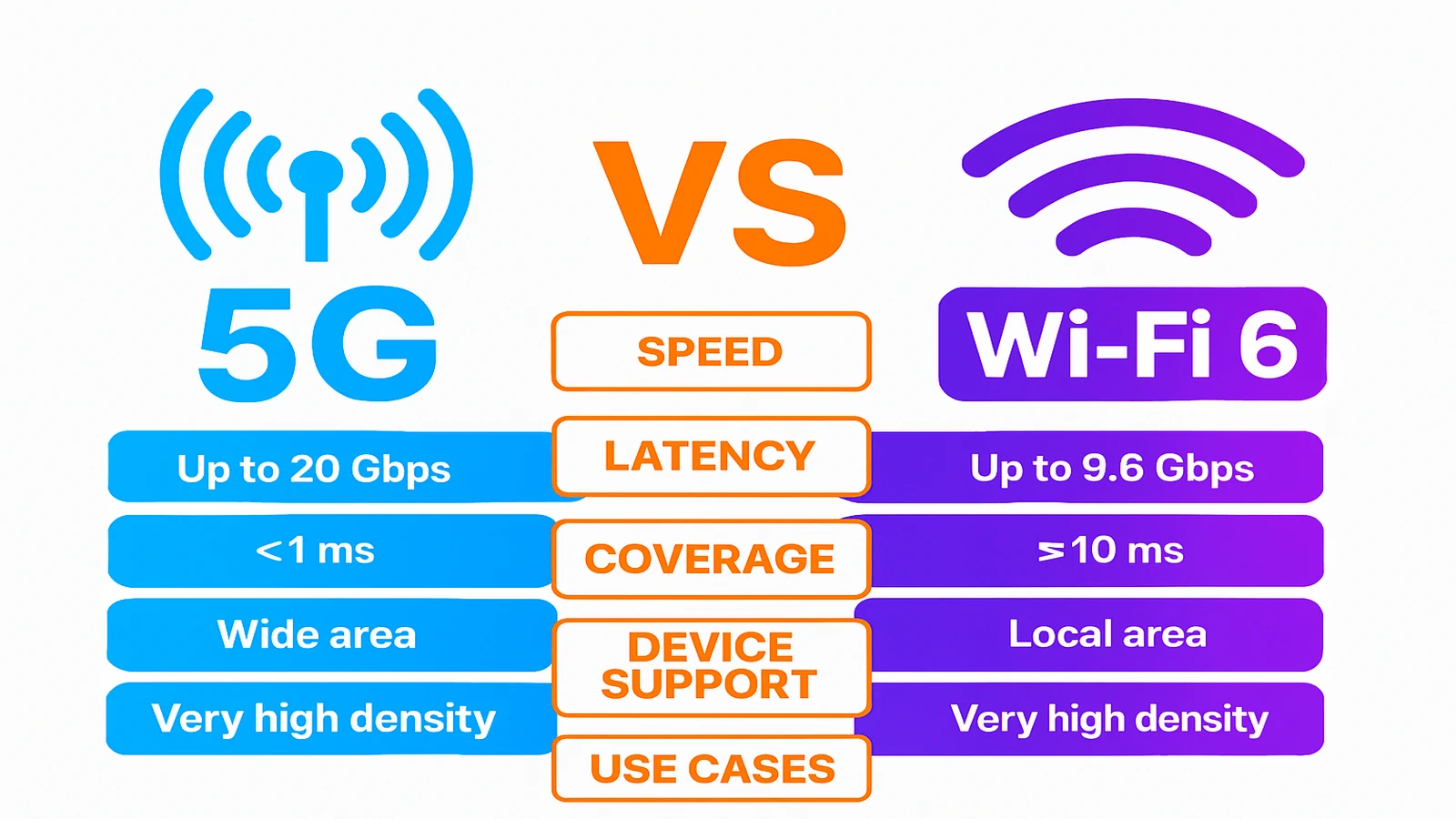
- Increased speed (up to 10 Gbps in optimal circumstances)
- Reduced latency (down to 1 ms)
- Increased bandwidth to link more devices simultaneously
5G also operates across multiple frequency bands:
- Low-band: Slower speeds but wider coverage
- Mid-band: Equilibrium speed and coverage
- High-band (mmWave): Extremely quick, but penetration and range are constrained
This implies that although 5G has the potential to be extremely fast, its effectiveness may differ depending on the region and type of 5G being used.
What is wi-fi 6

The most recent Wi-Fi generation is wi-fi 6, sometimes referred to as 802.11ax. It is superior to earlier versions in several crucial areas:
- Up to 9.6 Gbps of speed
- Improved efficiency in crowded spaces
- Reduced power usage and delay
- More space for devices connected to the same network
Wi-Fi 6 works perfectly in homes, workplaces, and public areas where numerous devices connect to a single router or access point
Speed: 5G vs wi-fi 6
In theory, 5G and wi-fi 6 are almost identical in terms of maximum speeds. Wi-Fi 6 peaks at 9.6 Gbps, while mmWave 5G can reach up to 10 Gbps. Real-world speeds, however, differ significantly:
- Generally speaking, 5G average download rates fall between 100 Mbps and 1 Gbps, based on the frequency band, region, and network congestion.
- Wi-Fi 6 typically delivers average speeds between 300 Mbps and 800 Mbps, especially when paired with fiber-optic internet and a high-quality router
Wi-Fi tends to deliver more constant speeds indoors, although 5G may outperform Wi-Fi 6 in terms of peak performance.
Latency: 5G vs wi-fi 6
For tasks requiring real-time responsiveness, such as video conferencing, gaming, or remote surgery, latency is essential.
- Especially in mmWave or ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC) scenarios, 5G latency can be as low as 1 millisecond.
- Although network tuning can reduce it, Wi-Fi 6 latency often ranges from 10 to 30 milliseconds
5G’s extremely low latency makes it the superior choice for time-sensitive apps or mobile gaming, particularly when utilizing cutting-edge technologies like network slicing and edge computing.
Coverage and range: 5G vs wi-fi 6
ALL TEXT: Experience good coverage with wi-fi 6
If you are choosing a network, you would want it to have a good range and get a signal everywhere.
- The normal range of wi-fi 6 is between 50 and 100 feet indoors, which equals the range of your router. Floors and walls can weaken the signal. Only within the confines of your building or property can mesh Wi-Fi systems increase coverage.
- 5G is a cellular network that uses mobile towers to provide countrywide coverage. While low and mid-band 5G provide more coverage at slower speeds, mmWave 5G has a relatively short range and needs line-of-sight to work at its best.
Cost considerations: 5G vs wi-fi 6
People and companies both consider cost a significant factor.
- 5G-enabled devices can be more costly, and using 5G usually requires a monthly mobile data contract. Some providers offer 5G internet for homes, although there can be installation costs and service restrictions.
- Purchasing a suitable router is a one-time expense for wi-fi 6 and can range from $100 to $300. It then uses your current internet service without charging you extra.
Wi-Fi 6 is a more affordable mobile network for the majority of consumers, particularly for use at home and in the workplace.
Security and safety: 5G vs wi-fi 6
No matter which network you use, make sure it’s secure and protects your devices from hackers.
- Wi-Fi 6 uses WPA3, the most recent and secure Wi-Fi encryption protocol. It defends against frequent threats like man-in-the-middle breaches and password guessing.
- With SIM-based encryption, network slicing, and secure authentication controlled by mobile carriers, 5G offers improved security. Developers designed it with IoT and mission-critical applications in mind.
Both provide robust protection, but they require appropriate setup and administration.
Applications: When to use the wireless technology

Image source: https://www.shutterstock.com/image-photo/wifi-internet-access-concept-man-using-2311098307
ALL TEXT: Use wi-fi 6 anywhere
Both of the internet connections are suitable for use in different cases. Here is when to use each as follows:
5G is ideal for:
- People who require quick internet access while on the road
- Remote employees in places without cable or fiber
- Commuters, tourists, and digital nomads
- Autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and industrial IoT
wi-fi 6 is ideal for:
- Households with numerous smart gadgets
- Schools and offices with high user traffic
- Configurations for gaming and broadcasting
- Indoor environments where a steady pace is essential
When at all feasible, use both; they work well together.
Conclusion:
Both 5G and wi-fi 6 stand out as strong technologies created to satisfy our increasing need for speed, efficiency, and dependability as we enter a more connected future. But deciding between them isn’t about picking a winner; rather, it’s about realizing how each meets particular needs. 5G is perfect for industries that need real-time data access while on the go, remote workers, and mobile users. It is ideal for smart cities, driverless cars, and those who are always on the go because of its wide-area coverage and extremely low latency.
Wi-Fi 6 excels in homes, workplaces, and crowded spaces where many devices compete for bandwidth. It continues to be the foundation of indoor wireless connectivity due to its increased effectiveness, speed, and affordability. In the end, combining the two technologies frequently yields the best results. Your phone may, for instance, use 5G when you’re outside, then automatically switch to Wi-Fi 6 when you get home. This smooth transition will become common as networks develop.

